You may have heard a lot about the Federal Reserve’s (Fed) upcoming actions and their potential impact on the housing market. Here’s what you need to know.
The Fed is meeting this week to determine the next move for the Federal Funds Rate, which influences how much it costs banks to borrow from one another. While this doesn’t directly set mortgage rates, it does have an indirect effect, often pushing mortgage rates higher or lower. So, if you’re considering buying or selling a home, you’re likely wondering how these decisions might impact mortgage rates and if there’s a potential drop in sight.
Here’s a brief overview of the key factors the Fed will weigh this week, and what they could mean for the housing market:
The Fed’s Focus: 3 Key Economic Indicators
Inflation Trends
You’ve probably noticed prices creeping up for everyday items—this is inflation at work. The Fed’s goal is to bring inflation closer to their 2% target. Although inflation is still above this level, it’s been moving downward over the past couple of years and has recently stabilized (see graph below).Job Growth
Another important factor is how many new jobs the economy is adding. A robust job market signals a healthy economy but can also contribute to inflation. The Fed monitors this balance closely, as stronger job growth can push inflation higher.Unemployment Rate
Lastly, the Fed considers the unemployment rate. Lower unemployment rates can drive consumer spending, which can, in turn, increase inflation. The Fed aims to keep this rate steady without fueling excessive price increases.
By keeping an eye on these indicators, you’ll get a sense of where the Fed may be headed with interest rates—and how this could impact mortgage rates in the near future.
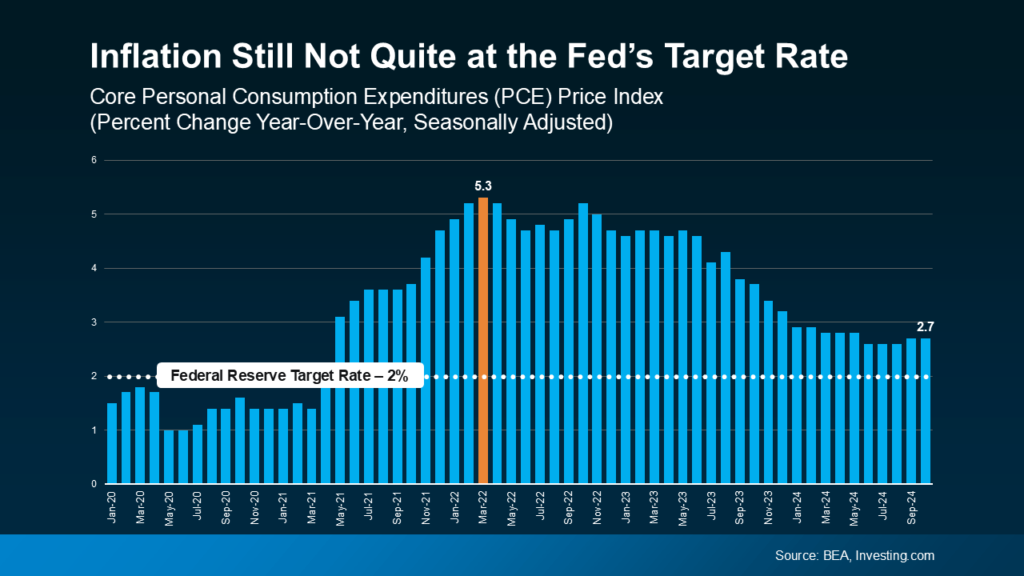
The Fed’s decisions this week are largely influenced by the current state of inflation, job growth, and unemployment. Here’s a look at what each of these indicators means for the Federal Funds Rate and the broader economy:
1. Inflation Trends
Although inflation is still above the Fed’s target rate, the recent downward trend suggests that we’re heading in the right direction. This progress is a key reason why the Fed may lower the Federal Funds Rate this week, aiming to make borrowing more affordable while supporting steady economic growth.
2. Job Growth
The Fed closely monitors job creation each month, as a gradual slowdown in job growth signals a cooling economy—exactly what they’re working toward. Recent data reflects this trend, with October’s job growth hitting its lowest point since December 2020, according to Reuters:
“Any doubts the Federal Reserve will go ahead with an interest-rate cut . . . fell away on Friday after a government report showed U.S. employers added fewer workers in October than in any month since December 2020.”
While employers are still hiring, the pace has slowed, indicating a natural cooling that aligns with the Fed’s goals.
3. Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate reflects the percentage of people seeking but unable to find work. Low unemployment generally signals a strong job market, but it can also push inflation higher, as more people earning means more spending, which drives up prices.
Economists often view an unemployment rate below 5% as close to full employment. Currently, the rate stands at 4.1% (see graph below), suggesting the labor market remains robust yet balanced.
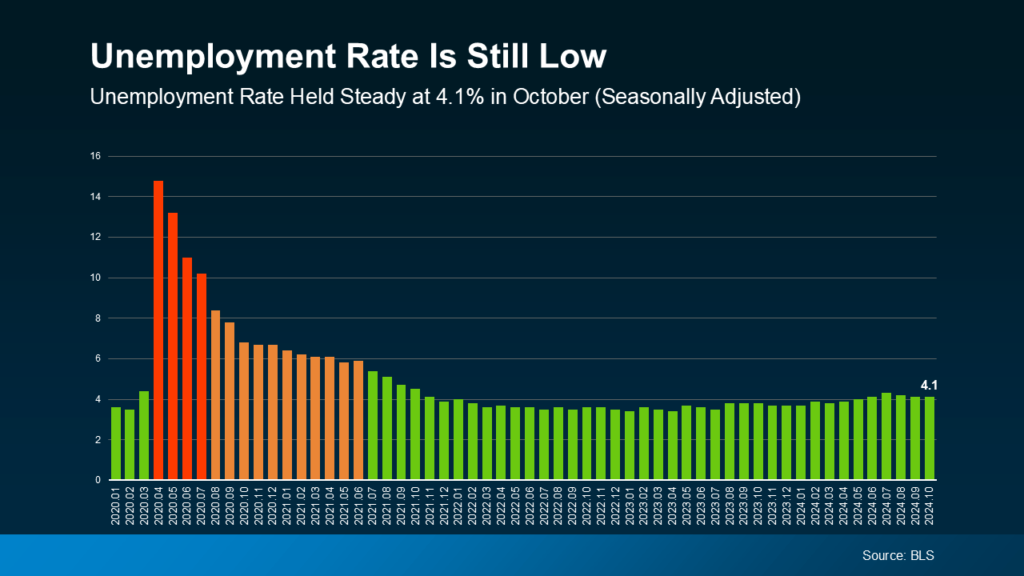
With unemployment remaining low, the labor market shows resilience even as job growth moderates—a balance the Fed has been aiming for.
What to Expect Going Forward
The economy is trending in the direction the Fed wants, which is why experts, including the CME FedWatch Tool, project a likely quarter-point reduction in the Federal Funds Rate this week.
If this cut happens as expected, it could eventually lead to a drop in mortgage rates, but don’t expect an immediate change. Mortgage rates typically adjust more gradually over time, often reflecting the broader economic picture. Forecasts suggest mortgage rates could ease through the next year, provided the key economic indicators continue to move favorably and the Fed proceeds with planned rate cuts into 2025.
However, any significant shifts in these indicators could lead to market adjustments and impact the Fed’s approach. Prepare for some volatility, as mortgage rates may fluctuate in response. Ralph McLaughlin, Senior Economist at Realtor.com, explains:
“The trajectory of rates over the coming months will be largely dependent on three key factors: (1) the performance of the labor market, (2) the outcome of the presidential election, and (3) any possible reemergence of inflationary pressure. While volatility has been the theme of mortgage rates over the past several months, we expect stability to reemerge towards the end of November and into early December.”
Bottom Line
While the Fed’s decisions are a factor, it’s the overall economic data and market conditions that ultimately drive mortgage rates. Looking ahead through the end of 2024 and into 2025, expect rates to stabilize or gradually decline, bringing some much-needed consistency to a turbulent market.




